Violence Impacts Teens’ Lives
Overview
Violence is preventable. We can all help young people grow up violence-free. Violence can limit life opportunities, lead to emotional and physical health problems, and shorten lives. Far too commonly, teens 14 to 18 years old experience violence, often more than one type such as physical fighting, sexual violence, dating violence, and bullying.
- Every day about 360 teens are treated in emergency departments for assault injuries.
- Homicide is the 3rd leading cause of death among teens.
- Female teens are more likely than males to experience three or more types of violence, as are sexual minority teens compared to their heterosexual peers.
- Some teens may have a higher risk of online bullying and threats during COVID-19.
- Violence can impact school attendance and access to community support services.
Teens who experience violence have several health conditions and risk behaviors, including:
- Missed school due to safety concerns
- Low academic grades
- Carried a weapon
- Suicidal thoughts or behavior
- Risky sexual behavior
- Overweight or obesity
- Felt sad or hopeless
- Substance use
As teens experience more violence, their health risks increase.
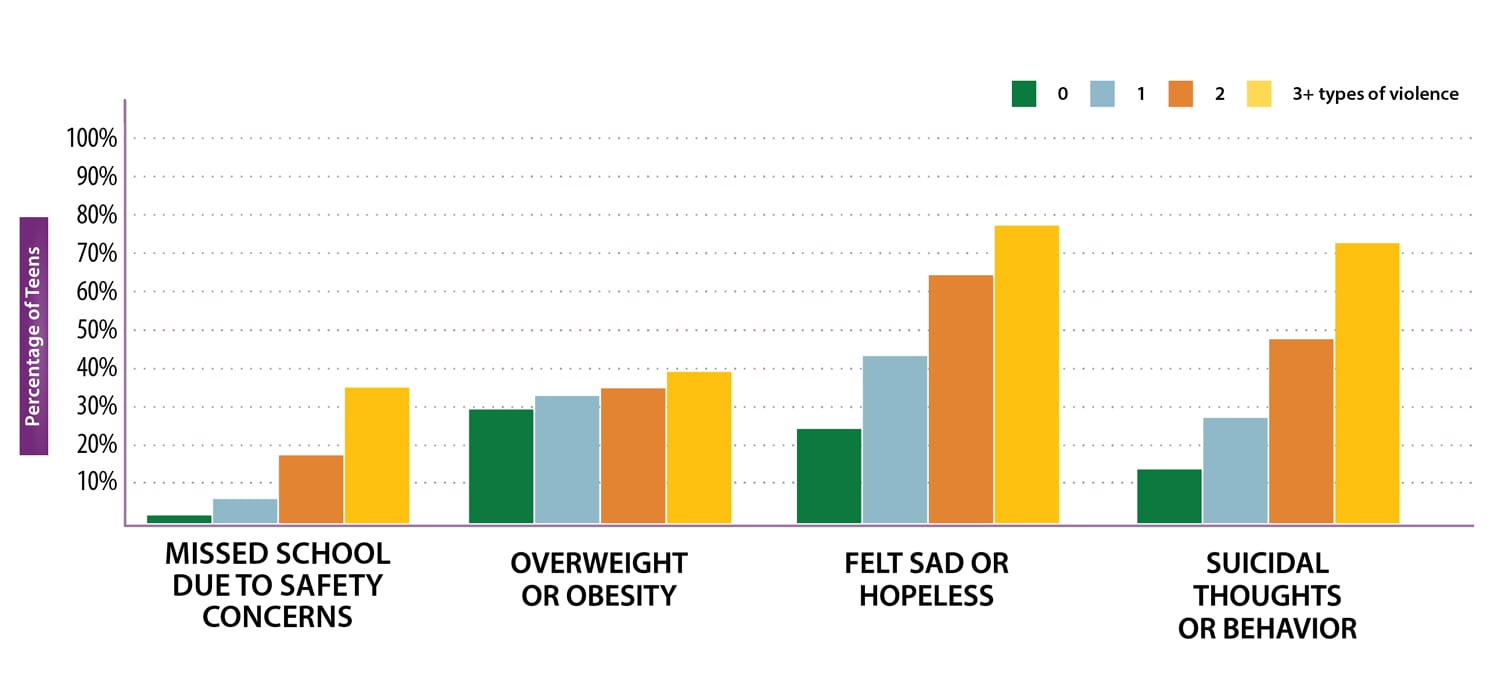
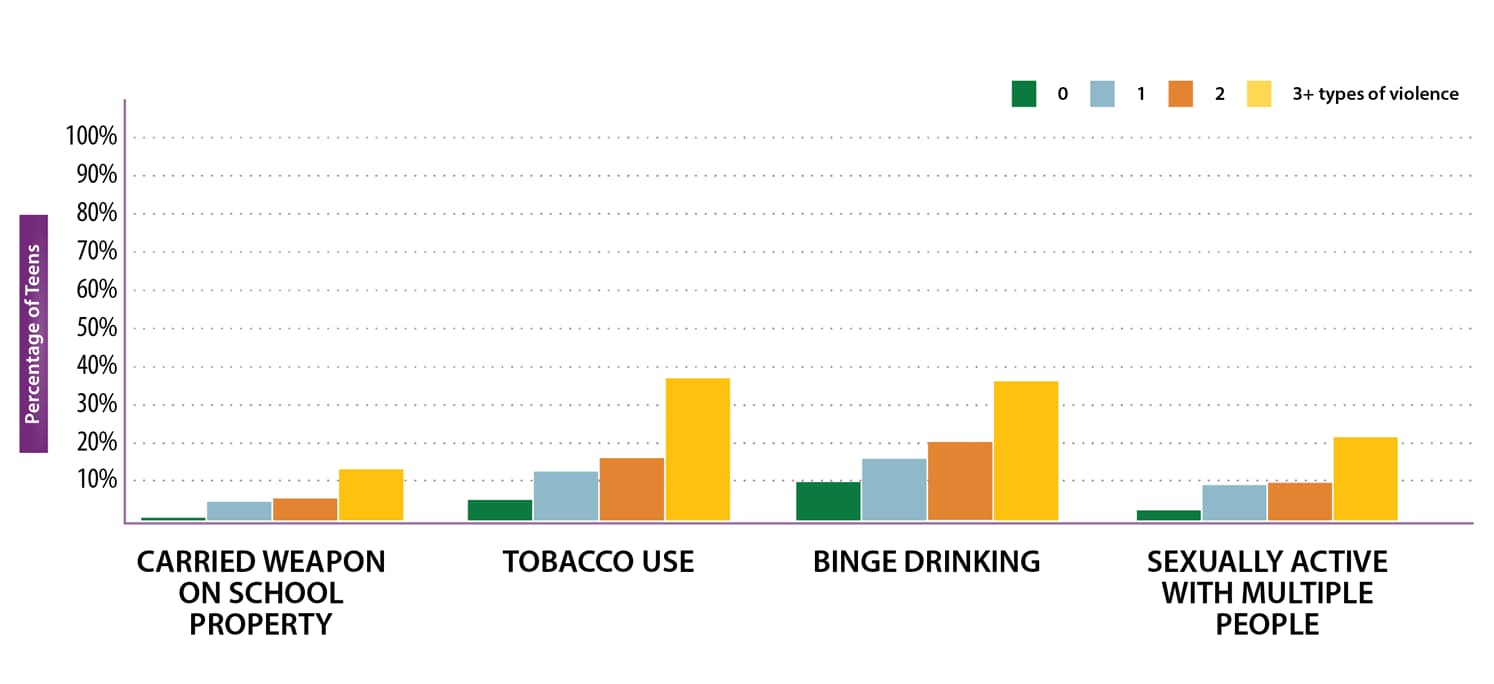
SOURCE: Youth Risk Behavior Survey, United States, 2019, CDC Vital Signs, MMWR February 2021.

Directly engaging teens in preventing violence helps them:
- Make healthy choices.
- Be a leader and voice for change for healthier communities and schools.
- Advise community and school decision-makers.
- Promote respect and empathy with family, friends, and peers.
Source: Centers for Disease Control
Articles posted on this site are the works of their respective authors. They may be for informational or entertainment purposes and do not necessarily represent the views of this website nor imply endorsement by this website, nor endorsement of this site by the authors, nor do we get paid for placing articles on this site. Please do your research and seek professional advice before using any information.

