The Crucial Role of Amino Acids in Brain Health: Functions, Significance, and Therapeutic Potential
By Editorial Team
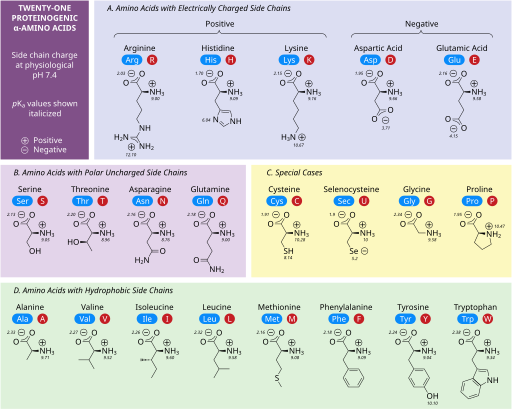
TungstenEinsteinium, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Amino acids play a crucial role in brain health and function. These organic compounds are the building blocks of proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of cells, including neurons in the brain. Amino acids are involved in various processes in the brain, such as neurotransmitter synthesis, energy production, and the regulation of gene expression. In this discussion, we will explore the importance of amino acids in brain health, their specific functions, and their potential use in treatments.
- Neurotransmitter Synthesis: Amino acids are precursors for the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons. For example, the amino acid tryptophan is converted into serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, sleep, and appetite. Similarly, the amino acid tyrosine is used to produce dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, which are involved in motivation, reward, and stress response.
- Protein Synthesis: Amino acids are fundamental for the synthesis of proteins in brain cells. Proteins are essential for various functions in the brain, such as the formation of synaptic connections, the maintenance of cell structure, and the regulation of enzymatic activity. Without an adequate supply of amino acids, the brain’s ability to produce and maintain proteins necessary for proper functioning is compromised.
- Energy Production: Amino acids can be utilized as an energy source in the brain. During periods of fasting or prolonged exercise, when glucose availability is limited, certain amino acids can be broken down and converted into intermediates of the energy-producing pathways. This helps ensure a continuous energy supply to the brain, which is vital for its proper functioning.
- Antioxidant Protection: Some amino acids, such as glutathione, serve as powerful antioxidants in the brain. They help neutralize harmful free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules that can damage cells and contribute to neurodegenerative diseases. Glutathione, in particular, plays a critical role in maintaining the overall redox balance and protecting neurons from oxidative stress.
- Neuroprotection and Neuroplasticity: Certain amino acids have been implicated in promoting neuroprotection and neuroplasticity, which are essential for maintaining brain health and preventing cognitive decline. For example, the amino acid acetyl-L-carnitine has been shown to enhance mitochondrial function, increase neuronal survival, and support cognitive function. Another amino acid, taurine, exhibits neuroprotective properties by regulating calcium homeostasis and reducing excitotoxicity.
- Treatment Applications: Amino acids have shown promise in the treatment of various brain-related conditions. For instance, the amino acid L-theanine, found in green tea, has been studied for its anxiolytic and calming effects. It can promote relaxation without inducing drowsiness and has been used as a complementary treatment for anxiety and stress-related disorders.
In certain neurological disorders, specific amino acid therapies have been explored. For example, in Parkinson’s disease, the administration of levodopa (L-dopa), an amino acid precursor of dopamine, is a standard treatment to replenish dopamine levels in the brain. In cases of phenylketonuria (PKU), a metabolic disorder that affects phenylalanine metabolism, dietary management involves strict restriction of phenylalanine intake to prevent cognitive impairment and neurological damage.
It’s important to note that while amino acids are essential for brain health, their supplementation or therapeutic use should be done under medical supervision. The balance and interaction of amino acids in the body are complex, and improper use or excessive intake may lead to unintended consequences. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals when considering amino acid supplementation or treatment approaches for brain-related conditions.
In conclusion, amino acids play a multifaceted role in brain health, including neurotransmitter synthesis, protein synthesis, energy production, antioxidant protection, neuroprotection, and neuroplasticity. Their functions are critical for maintaining proper brain function and preventing neurological disorders. The targeted use of specific amino acids in treatments holds promise for various brain-related conditions, but it should be approached with caution and medical guidance to ensure optimal benefits and minimize risks.
Nothing herein is intended to diagnose, treat or cure any disease. Please do your research and seek professional advice before using any information.